Written by Jesper Tingvall, Product Expert, Simplygon
本文由 Simplygon 產品專家 Jesper Tingvall 撰寫。
Disclaimer: The code in this post is written using version 9.1.36100 of Simplygon. If you encounter this post at a later stage, some of the API calls might have changed. However, the core concepts should still remain valid.
免責聲明:本文中的程式碼是使用 Simplygon 的 9.1.36100 版本撰寫的。如果您在以後的階段遇到這篇文章,部分 API 調用可能已經更改。但是,核心概念應該仍然有效。
Introduction 介紹
A common way of saving texture memory is to compress normal maps and just use two channels instead of three. In this example from Anno 1800, by Ubisoft Mainz, the blue channel of the normal map is used to store emissive data. This blog post describes how to create a shading network allowing Simplygon to optimize such assets. In our case we will aggregate two adjacent models to reduce draw calls.
節省紋理記憶體的常見方法是壓縮法線貼圖,只使用兩個通道而不是三個。在 Ubisoft Mainz 的 Anno 1800 中的這個例子中,法線貼圖的藍色通道用於存儲發光數據。本博客文章描述了如何創建一個著色網絡,使 Simplygon 能夠優化這樣的資產。在我們的案例中,我們將聚合兩個相鄰的模型以減少繪製呼叫。

Prerequisites 先決條件
This example will use the Python Simplygon integration in 3ds Max, but the same concepts can be applied to all other integrations of the Simplygon API.
這個範例將在 3ds Max 中使用 Python Simplygon 整合,但相同的概念也可以應用於 Simplygon API 的所有其他整合。
Problem to solve 問題要解決
The asset we want to optimize with Simplygon have a normal map where the blue channel contains emissive data.
我們希望用 Simplygon 優化的資產具有一個帶有發光數據的法線貼圖,其中藍色通道包含發光數據。
Solution 解決方案
The solution is to create a custom shading network which can recreate the entire normal map and create an emissive channel.
解決方案是創建一個自定義的著色網絡,可以重新創建整個法線貼圖並創建發光通道。
Normal map encoding 法線貼圖編碼
A normal's component values goes from -1 to 1. However when it is saved to an RGB texture it can not have negative color values. Thus the input range is 0->1 instead of -1->1. Before we do any processing we need to expand it so it covers the entire range. This can be done with the formula normal_map_in_correct_range = input_normal_map * [2, 2, 2, 1] - [1, 1, 1, 0]. The constants can either be ShadingColorNodes or default parameters in the multiply and subtraction nodes.
法線的分量值範圍從-1 到 1。但是,當它保存到 RGB 紋理時,不能具有負的顏色值。因此,輸入範圍為 0->1,而不是-1->1。在進行任何處理之前,我們需要擴展它以涵蓋整個範圍。這可以使用公式 normal_map_in_correct_range = input_normal_map * [2, 2, 2, 1] - [1, 1, 1, 0] 完成。常數可以是 ShadingColorNodes 或乘法和減法節點中的默認參數。
With ShadingColorNodes the constants are more clear and can be labeled.
使用 ShadingColorNodes 可以使常數更清晰並且可以標記。
With default parameters the code is more dense. This is the style we are going to use in the rest of the script.
使用默認參數可以使代碼更緊湊。這是我們將在腳本的其餘部分中使用的風格。
After processing the normal map we need to encode it back from -1->1 to 0->1 range. This can be done with the formula output_normal_map = (processed_normal_map + [1, 1, 1, 0]) * [0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 1].
經過處理法線貼圖後,我們需要將其從 -1->1 範圍編碼回 0->1 範圍。這可以通過公式 output_normal_map = (processed_normal_map + [1, 1, 1, 0]) * [0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 1] 完成。
Recreating blue channel from red and green channels
重新創建藍色通道,從紅色和綠色通道
Since the normal map describes a vector of length one we can recreate the blue value from just knowing red and green value by the formula blue = sqrt(1 - red*red - green*green). This can be realized by the following shading network.
由於法線貼圖描述了長度為一的向量,我們可以通過僅知道紅色和綠色值來重新創建藍色值,公式為 blue = sqrt(1 - red*red - green*green) 。這可以通過以下著色網絡實現。
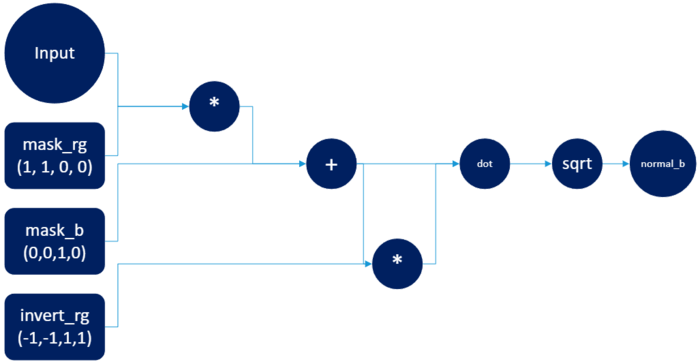
After calculating the blue channel it needs to be merged together with red and green channels to create the full normal map.
計算藍色通道後,需要將其與紅色和綠色通道合併,以創建完整的法線貼圖。
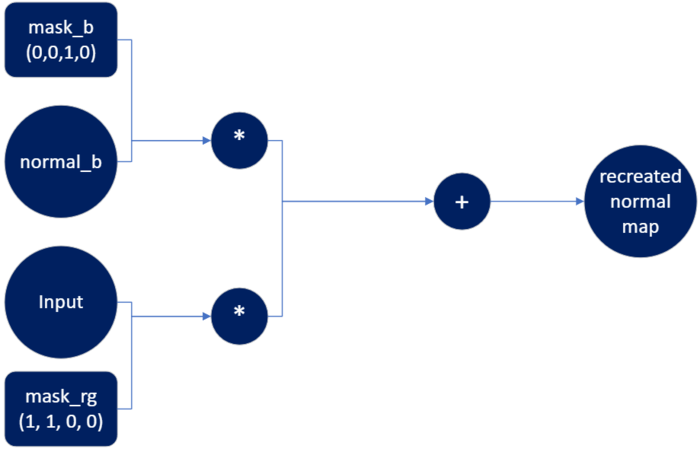
Here is the corresponding code to generate both shading networks.
這是用於生成兩個著色網絡的相應代碼。
Emissive shading network
發光著色網絡
To create the emissive map we need to take the blue color from the input normal map and create a black and white image from it.
為了創建發光貼圖,我們需要從輸入法線貼圖中提取藍色,並從中創建一幅黑白圖像。
Normal caster 普通魔法師
With the shading network describing how to recreate the normal map we can use a NormalCaster to generate our normal map. Make sure to set the NormalCasterSettings to correspond to your game engine.
Emissive caster
A ColorCaster can be used to generate the emissive map.
Result
The resulting shading network allows Simplygon to optimize assets where the normal map is compressed. It outputs an ordinary normal map and emissive texture. These textures can then be fed back into the texture optimization toolchain.
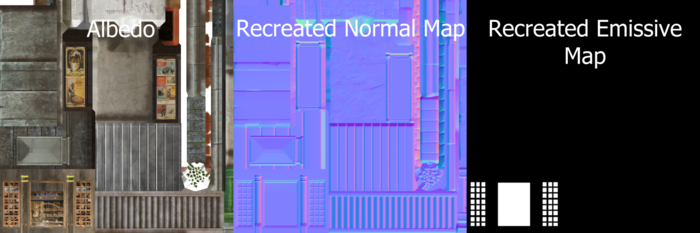
Complete script
The following script exports all objects from 3ds Max, runs an aggregation and reimports result. It recreates blue channel in a compressed normal map and creates an emissive textures from the blue channel. Depending on your game engine you might need to change tangent space method using SetGlobalDefaultTangentCalculatorTypeSetting.
from pymxs import runtime as rt
from simplygon import simplygon_loader
from simplygon import Simplygon
import gc
def encode_normal(sg, input):
positive = sg.CreateShadingAddNode()
positive.SetInput(0, input)
positive.SetDefaultParameter(1, 1, 1, 1, 0)
normal = sg.CreateShadingMultiplyNode()
normal.SetInput(0, positive)
positive.SetDefaultParameter(1, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5,1)
return normal
def decode_normal(sg, input_node):
doubled = sg.CreateShadingMultiplyNode()
doubled.SetInput(0, input_node)
doubled.SetDefaultParameter(1, 2, 2, 2, 1)
output = sg.CreateShadingSubtractNode()
output.SetInput(0, doubled)
output.SetDefaultParameter(1, 1, 1, 1, 0)
return output
def regenerate_blue_normal_channel(sg, input_node):
input_rg = sg.CreateShadingMultiplyNode()
input_rg.SetInput(0, input_node)
input_rg.SetDefaultParameter(1, 1,1,0,0)
input_rg1 = sg.CreateShadingAddNode()
input_rg1.SetInput(0, input_rg)
input_rg1.SetDefaultParameter(1, 0,0,1,0)
invert_rg1 = sg.CreateShadingMultiplyNode()
invert_rg1.SetInput(0, input_rg1)
invert_rg1.SetDefaultParameter(1, -1, -1, 1, 1)
dot = sg.CreateShadingDot3Node()
dot.SetInput(0, input_rg1)
dot.SetInput(1, invert_rg1)
bbb = sg.CreateShadingSqrtNode()
bbb.SetInput(0, dot)
b = sg.CreateShadingMultiplyNode()
b.SetInput(0, bbb)
b.SetDefaultParameter(1, 0, 0, 1, 0)
input_rga = sg.CreateShadingMultiplyNode()
input_rga.SetInput(0, input_node)
input_rga.SetDefaultParameter(1, 1, 1, 0, 1)
output = sg.CreateShadingAddNode()
output.SetInput(0, b)
output.SetInput(1, input_rga)
return output
def create_emissive_network(sg, input_node):
emissive = sg.CreateShadingDot3Node()
emissive.SetInput(0, input_node)
emissive.SetDefaultParameter(1, 0, 0, 1, 0)
return emissive
def run_pipeline(sg, import_path, processed_path, textures_path):
sg.SetGlobalDefaultTangentCalculatorTypeSetting(Simplygon.ETangentSpaceMethod_Autodesk3dsMax)
sceneImporter = sg.CreateSceneImporter()
sceneImporter.SetImportFilePath(import_path)
sceneImporter.RunImport()
scene = sceneImporter.GetScene()
material_count = scene.GetMaterialTable().GetMaterialsCount()
for i in range(0, material_count):
print('Creating shading network for material ',i)
material = scene.GetMaterialTable().GetMaterial(i)
normal_input = material.GetShadingNetwork("bump")
if normal_input is not None:
normal = decode_normal(sg, normal_input)
regenerated_normal = regenerate_blue_normal_channel(sg, normal)
recoded_normal = encode_normal(sg, regenerated_normal)
material.SetShadingNetwork("bump", recoded_normal)
emissiveNode = create_emissive_network(sg, normal_input)
material.SetShadingNetwork("emit_color", emissiveNode)
pipeline = sg.CreateAggregationPipeline()
pipeline.GetPipelineSettings().SetTextureOutputPath(textures_path)
mapping_image_settings = pipeline.GetMappingImageSettings()
mapping_image_settings.SetGenerateMappingImage(True)
mapping_image_settings.SetTexCoordName("MaterialLOD")
mapping_image_settings.SetTexCoordGeneratorType( Simplygon.ETexcoordGeneratorType_ChartAggregator )
sgChartAggregatorSettings = mapping_image_settings.GetChartAggregatorSettings()
sgChartAggregatorSettings.SetChartAggregatorMode( Simplygon.EChartAggregatorMode_SurfaceArea )
sgChartAggregatorSettings.SetSeparateOverlappingCharts( False )
material_settings = mapping_image_settings.GetOutputMaterialSettings(0)
material_settings.SetTextureWidth(2048)
material_settings.SetTextureHeight(2048)
caster = sg.CreateColorCaster()
caster_settings = caster.GetColorCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel("base_color")
pipeline.AddMaterialCaster( caster, 0 )
caster = sg.CreateNormalCaster()
caster_settings = caster.GetNormalCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetGenerateTangentSpaceNormals(True)
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel("bump")
pipeline.AddMaterialCaster( caster, 0 )
caster = sg.CreateColorCaster()
caster_settings = caster.GetColorCasterSettings()
caster_settings.SetMaterialChannel("emit_color")
pipeline.AddMaterialCaster( caster, 0 )
print("Running remeshing process...")
pipeline.RunScene(scene, Simplygon.EPipelineRunMode_RunInThisProcess)
scene_exporter = sg.CreateSceneExporter()
scene_exporter.SetExportFilePath(processed_path)
scene_exporter.SetScene(scene)
scene_exporter.RunExport()
print('LODS done!')
def cleanup():
rt.sgsdk_ClearGlobalMapping()
rt.sgsdk_Reset()
def export_scene(path):
rt.select(rt.objects)
bResult = rt.sgsdk_ExportToFile(path, False)
def import_scene(path):
print('Importing...')
rt.sgsdk_SetInitialLODIndex(1)
rt.sgsdk_SetMeshNameFormat('{MeshName}_LOD{LODIndex}')
bResult = rt.sgsdk_ImportFromFile(path, True, True, True)
print('Import result: ', bResult)
def main(argv):
export_path = 'C:/Temp/ExportedScene.sb'
processed_path = 'C:/Temp/ProcessedScene.sb'
textures_path = 'C:/Temp'
cleanup()
export_scene(export_path)
sg = simplygon_loader.init_simplygon()
run_pipeline(sg, export_path, processed_path, textures_path)
import_scene(processed_path)
sg = None
gc.collect()
print('End')
if __name__== "__main__":
main(sys.argv[1:])






